The Epic History Behind Ludo
Ludo is one of the most beloved board games of many people across the world, alongside others like reversi and backgammon.
The rules are simple, and the cross and circle arrangement of the board is recognizable regardless of the names under which the game is known. But did you know this game has ancient, epic origins?
Chaupar: The Game of Royalty
While different circle games have been found in ancient cultures across the world, Ludo and its multiple variants derive from Pachisi, the national game of India. Like Ludo, the game of pachisi can be played with two to four players. The game consists of a cross and circle board where players must move their pieces counterclockwise around the board and return to the center. Some traditional versions of the game use cowrie shells instead of dice.
Pachisi can be traced back to 6th century India. This game was likely inspired by an ancient game called chaupar, which is mentioned in the sacred epic of the Mahabharata. This epic tale tells the story of a war between two families: the Pandavas and the Kauravas. During a game of chaupar, prince Shakuni from the Kauravas uses cursed dice to win the game and take the Pandavas’ fortune, triggering a war between both families.
Centuries later, one of the first historical records of chaupar comes from the Mughal Empire, in the 16th century. According to historian Louis Rousselet, the Mughal emperor Akbar would use members of his court dressed in different colors as pieces that he and his opponents would move on a life-sized board. Traces of these boards can be found in the palace of Fatehpur Sikri in the city of Agra.
The name of the game that we know nowadays as pachisi comes from the Hindi “pacis” which means “twenty-five.” This name comes from the fact that in pachisi the highest score you can get from throwing the cowrie shells is precisely twenty-five (thirty in some versions). This game has been so popular in India that with the arrival of the British Empire, the game arrived in England and was patented in 1896 under a new name: Ludo.
The Differences between Ludo and Pachisi
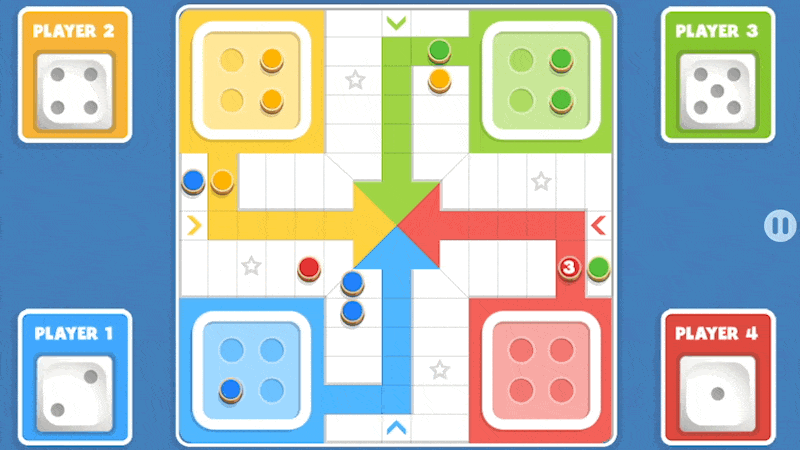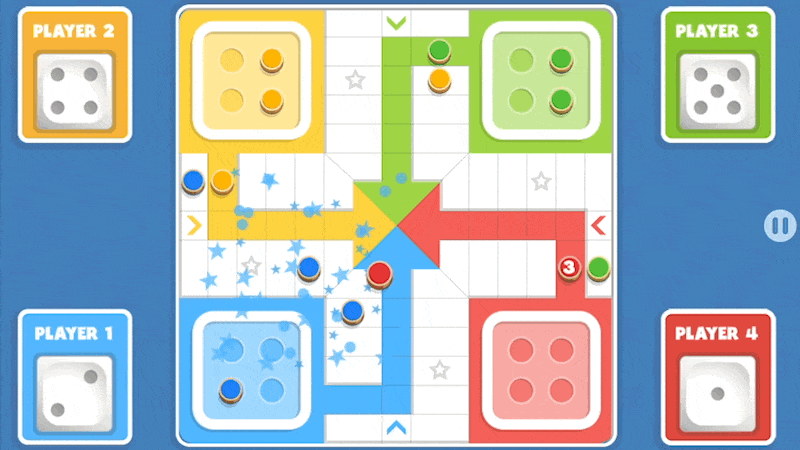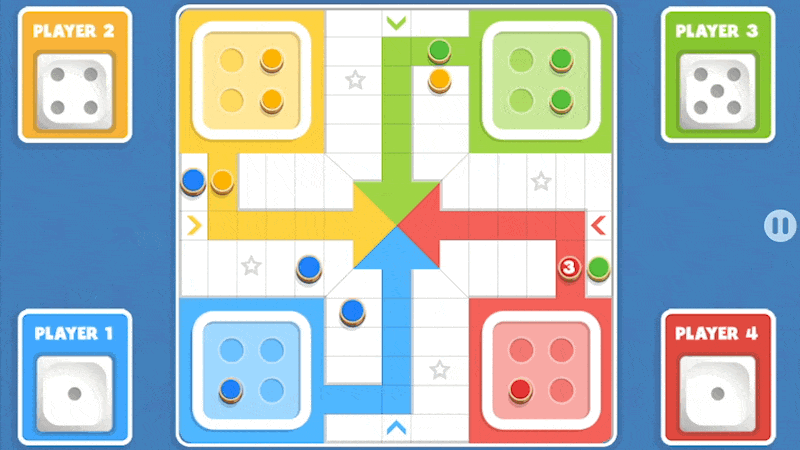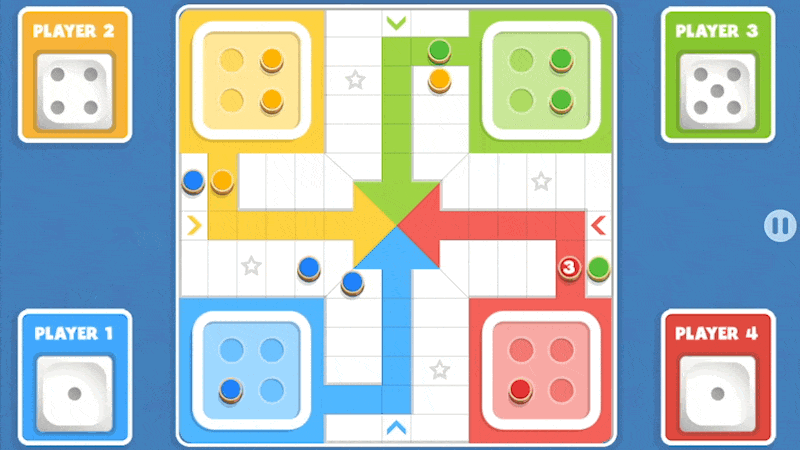
When Ludo was patented in the United Kingdom, it was intended to be a simpler version of pachisi for children and families. Even though both are very similar games, there are key differences in their gameplay:
The board
While Ludo was introduced as a cardboard-based board, pachisi has been traditionally played on embroidered cloth boards. Of course, nowadays both games can be found in different presentations, ranging from cardboard and plastic boards to online versions, like Ludo Legend.
Dice
As we mentioned before, pachisi uses cowrie shells with different values, which allow the player to score up to twenty-five points. Ludo, however, uses a single die, and its first editions included a dice cup alongside the board.
Start
In pachisi, all players start at the center of the board, and if they roll 6, 10, or 25 they are allowed to introduce a piece to the board. In Ludo, however, the player’s token starts on color yards and is allowed to introduce a new piece into the board whenever the die rolls 6.
Passes
Ludo players are not allowed to skip turns, whereas, in pachisi, players can opt to pass. This possibility adds another layer of complexity to pachisi since players can use this as a strategy to move and keep the pieces on the board.
The creation of Ludo opened the doors to multiple versions of the game in the 20th century. One of these versions is Uckers, a popular game in the British royal navy, where players use two dice instead of one and a larger board.
Parcheesi and other names
Pachisi not only made its way to the United Kingdom, but it crossed to America in the 1860s, where it eventually was patented as Parcheesi by the Parker Brothers and Winning Moves Games. The game shares similarities with both Ludo and pachisi, except that the board looks closer to pachisi, and it is played with two dice instead of one.
With the trademark of Parcheesi, new versions of the game appeared in other parts of the world. For instance, in the United States, the game was released as Aggravation by Hasbro. In other countries, the game has been known under different names such as parqués in Colombia, parchis in Spain, men's-erger-Je-niet (Man, Don’t Get Angry) in Dutch, among others.
Throughout the history of board games, none has been as influential as Ludo. From a sacred game of heroes and kings to a game to share with family and friends, Ludo ranks among the unforgettable games like chess and checkers. If you want to learn the history of these timeless games, check out the following posts: